Alkylation of cresols to BHT
Summary of the work made
We have studied the production of Butylated Hydroxy Toluene (BHT), an important anti-oxidant, in the presence of an acid exchange resin as catalyst, by considering both the kinetics of all the occurring reactions and all the mass transfer contributions. The reaction has been studied by using two different type of reactors: a well mixed semibatch reactor and a spray tower loop reactor. The spray tower loop reactor is a good choice preventing the gas-liquid mass transfer limitation.
Work
Butylated Hydroxy Toluene (BHT) is a substance largely employed as antioxidant. BHT is produced by alkylation of p-cresol with isobutene.
The reaction promoted by acid catalysts occurs in two steps that are:
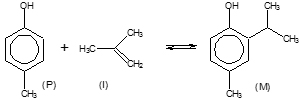
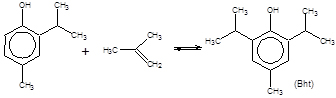
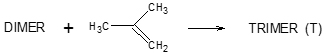
Isobutene oligomerizations also occur as side reactions, such as:
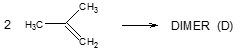
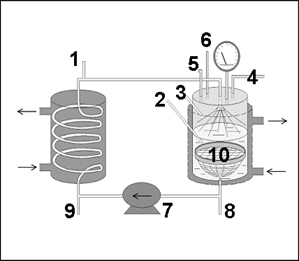
Scheme of the used Spray Tower Loop Reactor: (1) sampling line; (2) liquid temperature; (3) gas temperature; (4) flow meter; (5) pressure transducer; (6) safety valve; (7) gear pump; (8,9) drain line (10) catalyst basket.
All the reactions are promoted by acid catalysts. We have deeply studied the production of BHT in the presence of an acid exchange resin as catalyst by considering both the kinetics of all the occurring reactions and all the mass transfer contributions. The reaction has been studied by using two different type of reactors: a well mixed semibatch reactor [1] and a spray tower loop reactor [2].
-
E. Santacesaria, R. Silvani, P. Wilkinson, S. Carrà; "Alkylation of p-Cresol with isobutene catalyzed by cation- exchange resins: a kinetic study". Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 27, 541 (1988).

-
Santacesaria, Elio; Di Serio, Martino; Tesser, Riccardo; Cammarota, Francesco; “ Comparison between the Performances of a Well-Stirred Slurry Reactor and a Spray Loop Reactor for the Alkylation of p-Cresol with Isobutene.” Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research (2005), 44(25), 9473-9481.
